“Next-generation batteries” are the key technology for innovation evolution.Why Softbank develops batteries
Batteries are indispensable for the diversification of mobile devices, not just smartphones and personal computers. Japan has long been a world leader in the field of battery development such as lithium-ion batteries and nickel-metal hydride batteries, but as each country declares a shift to EV with the goal of reducing CO2, the battle for supremacy in battery development was in the Warring States period. It seems that it is rushing.
Softbank is taking on the challenge of developing next-generation batteries, saying that it will "overturn common sense" in such a harsh market. You wonder, "Why are telecommunications companies developing batteries?" So I interviewed the person in charge about what kind of efforts they are doing.
People working on the development of next-generation batteries at Softbank
Softbank Technology-Unit Technology Strategy Management Advanced Technology Development Headquarters Advanced Technology Laboratory Energy Promotion Section
Takaya Saito, General Manager in charge
Joined Softbank in 2018 after being involved in research and development and mass production of lithium-ion secondary batteries for in-vehicle use at several major battery manufacturers.Currently, he is also involved in the procurement and development of next-generation batteries while concurrently serving as the battery development business of HAPS Mobile Co., Ltd.
Yoshiki Takayanagi
Joined a new graduate in 2019. After joining the company, he will be involved in research on lithium-air batteries.Since then, he has been involved in the procurement and development of next-generation batteries while concurrently serving as the battery development business of HAPS Mobile Co., Ltd.
His top priority is to achieve high weight energy density.Softbank battery development that dares to explore unique possibilities
Chemical batteries such as so-called dry batteries are divided into two categories, and lithium-ion batteries are currently said to be the most advanced secondary batteries.
The four main performance indicators of batteries are as follows.
① High energy density (lightening)
② Battery life
③ Safety
④ Cost
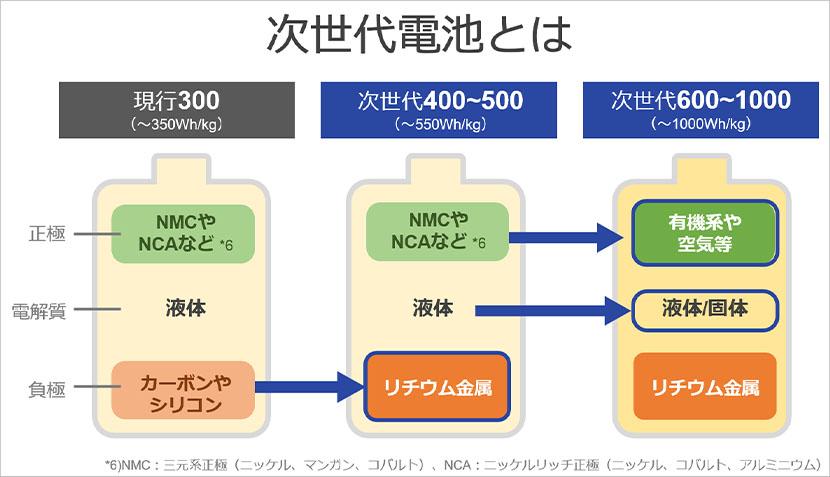
“Next-generation batteries” are batteries that can significantly improve and improve these performance aspects. Among them, Softbank is working on the development of "lithium metal batteries," which are ahead of lithium-ion batteries, with a particular focus on (1) high energy density (lightening).
Current lithium-ion secondary batteries use graphite, which has a low energy density, as the main material for the negative electrode, but next-generation batteries use a lithium metal material, which has a very high energy density, for the negative electrode, making them lighter. increase. Furthermore, efforts have begun to enable the use of organic systems (compounds mainly composed of light elements such as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) and air electrodes, which are theoretically expected to have high energy, at the positive electrode.
Battery development in Japan is progressing with a focus on (2) battery life and (3) safety, but SoftBank is particular about battery development, which is half the weight of conventional batteries and has the same energy (Wh). The weight energy density of existing batteries is about 250Wh / kg, but we are aiming to develop high energy densities of 1,000Wh / kg and 1,000Wh / L. It is also an initiative to develop next-generation batteries to find the optimum materials for the positive and negative electrodes of batteries.
Difference between Wh / kg and Wh / L
The units of weight energy density and volumetric energy density are used to compare the weight and outer diameter of a battery, both of which represent energy density.
-Wh / kg and Wh / L indicate the unit weight and the capacity of the battery per unit volume, respectively.
For example, lithium-ion batteries have the highest weight and volume energy densities compared to other batteries, about 2.5 times higher than nickel-metal hydride batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are the smallest and lightest batteries for the same energy and are used as power sources for mobile devices because they can be configured as small, lightweight and high energy density batteries.
For more information on smartphone batteries, from the basics of electricity such as voltage and current to the mechanism of charging, please see here.
What kind of unit is "mAh"?Basic knowledge of smartphone battery capacity that you should know
Batteries are the key technology for new industries.Batteries evolve to create great applications
What will next-generation batteries enable?
Due to its high capacity and light weight, we believe that new equipment will be developed to expand the area of human activity. EVs are expected to become widespread due to increased mileage, CO2 reduction, and cost reduction, and for example, cars flying in the sky due to the weight reduction of batteries. If this can be done, it will lead to the reduction of traffic congestion and the solution of emergency transportation problems for patients.
Then a drone that can fly for a long time. The distance traveled by drones will be extended, and it will be possible to deliver to depopulated areas and remote islands that could not be delivered until now.
The maximum energy of existing batteries is only 250Wh / kg. We believe that even greater innovation will occur as the number of devices and products (applications) equipped with 1,000 Wh / kg lightweight batteries, which we are aiming for, increases.
What other uses can you expect?
The lighter the battery, the higher the affinity with wearable terminals. It can be installed in places where it could not be installed due to its weight, and the number of locations where distributed batteries can be installed can be increased. In addition, it will be possible to extend the operating time of the backup power supply, which will contribute to disaster response such as preparation of disaster prevention equipment.
A prototype battery using elemental technology jointly developed by Softbank with Enpower Greentech Inc.
It has a thin shape with positive and negative electrodes stacked, and the exterior is laminated, making it lighter than conventional batteries.
