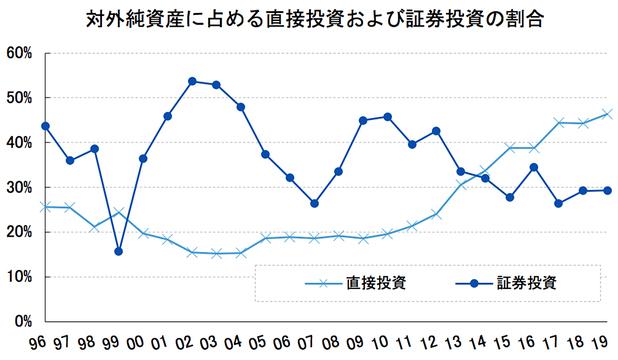
Japan is the country with the largest net foreign assets…Actual situation of net foreign assets in the whole world (latest version as of 2022)
Wealth on a country-by-country basis is indicated by net foreign assets of a particular country to other countries, net of debts and credits. Based on the value published by the IMF, we will confirm the actual situation in the world as a whole.
Net foreign assets are the sum of foreign assets and foreign liabilities. As a rough explanation, it is "Assets: things that are lent overseas in various forms" and "Liabilities: things that are borrowed from overseas in various forms."
The following are the values for countries whose net foreign assets can be confirmed in the IMF database, and those that have the latest available yearly figures for 2020, and those that do not have available figures for 2005. The top and bottom countries are extracted from a total of 174 countries applying the latest values after 2019. As shown in the original data, the values converted to US dollars are used. In the bottom row graph, the country with the most debt is on the left.
The United States has the largest net external debt in the world. Next is Spain, but the amount of the United States is too large and the graph is unbalanced. The difference between the United States and Spain is more than 10 times.
After Spain, England, France, Ireland, Australia, Mexico, Brazil and Turkey. Some countries are experiencing economic difficulties, and some people have the impression that this is the case.
On the other hand, it was Japan that had the largest net foreign assets, even after scrutinizing the whole world. Germany, Hong Kong and China follow. These four countries have over $2 trillion in net foreign assets. Followed by Norway, Netherlands, Canada and Singapore.
Since the bottom of each graph is minus $0.094 trillion and plus $0.091 trillion, the rest of the countries are between plus $0.090 trillion and minus $0.093 trillion.
This net foreign asset is the sum of public and private assets, and the asset portion cannot be immediately converted into cash. The addition of assets and liabilities when calculating net worth does not make much sense. Needless to say, it should be kept in mind that this is only an overview of the financial situation of individual countries, and that it is no more than reference material for seeking to improve the situation.
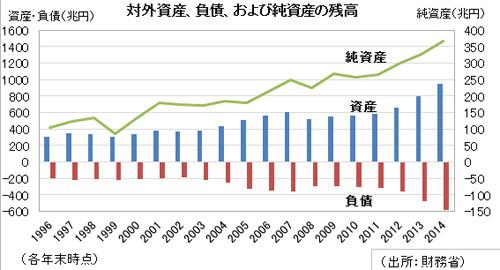
On the other hand, it must be unhealthy to emphasize only debts to arouse anxiety, or to present only assets to appeal the soundness. When there are such stories, the actual situation of net foreign assets in this case will be of great help.
■Related articles:
[Recently, 1 dollar is 113.19 yen, and the highest yen is 76.30 yen... Changes in the yen-dollar exchange rate (latest)]
[[Updated] If commodity prices continue to decline next year due to deflation, is it “worried” or “happy”?]
(Note) Unless otherwise specified, the graphs and charts in the text are quoted from or created by the author based on the materials.
(Note) Unless otherwise noted, the photographs in the text were created by the author based on the materials described in the text, or were taken by the author during interviews.
(Note) Numbers used in article titles, text, graphs, etc. may be written after rounding off any digits after the decimal point so that the display is considered optimal on the spot. I have. Therefore, the total number of figures on the display may not match exactly.
(Note) If the value at the end of the axis of the graph is set to a positive value other than zero in order to fix the appearance of the graph and make it easier to see the movement of the numbers, the value is enclosed in a circle or the like to call attention to it. There are cases.
(Note) In order to improve the appearance of the graph, some notation of items (such as okurigana) may be omitted or changed. Also, "~" may be expressed as "-".
(Note) "ppt" in the graph means % points.
(Note) "(Great) Earthquake" refers to the Great East Japan Earthquake unless otherwise specified.
(Note) This article is a partial addition and change to the article published in [Garbage News].
