
What are the security risks and countermeasures in local 5G introduction in the manufacturing industry?
Mr. Yohei Ishihara, Security Evangelist, Global IoT Marketing Office, Trend Micro
The core network is an infrastructure that is unfamiliar to corporate IT personnel, but it requires a control plane and a user plane that processes data, so if targeted by a cyber attacker, various attacks are possible. Therefore, this time, a demonstration experiment was conducted assuming an intrusion into the core network. The demonstration experiment was conducted assuming a steel industry that builds and operates the core network and RAN on their own.
Four Intrusion Routes in the Core Network
Mr. Ishihara is concerned about four intrusion routes in implementing the demonstration experiment, as it is possible to introduce general-purpose hardware and software into the core network. explained that it would be
The first entry point is the core network hosting server. By using x86 servers, there is a possibility that vulnerabilities in the OS can be exploited.
The second entry point is virtual machines and containers. Core network services utilize virtualization technology, which can create vulnerabilities.
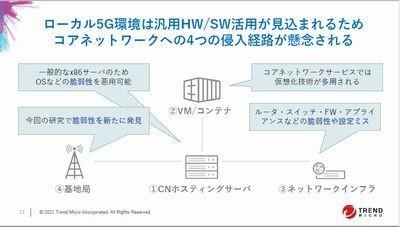
The third entry point is network infrastructure. Vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in routers and switches may allow attackers to invade. The fourth intrusion route is the base station, but it is said that a new vulnerability was discovered in this demonstration experiment. Ishihara said that when he informed the vendor of the base station's vulnerability, it turned out that it was sold as a verification package. Mr. Ishihara advised, "Because 5G-related products are not as open as IT products, we need to be careful about vendor responses."
Five Attack Techniques Targeting the Core Network
Next, Mr. Ishihara said that he identified three locations within the core network where data could be intercepted. The places are "between core network and Internet", "user plane server" and "between base station and core network". Even inside the core network, if communication is not encrypted, it becomes a risk.
In the demonstration experiment, we used five attacks against these three points: "MQTT hijacking", "Modbus/TCP hijacking", "PLC firmware reset", "DNS hijacking", and "remote desktop exploitation". method was performed.
For example, in the core network, there is a risk of destroying products and manufacturing processes by attacking communication using the MQTTMQTT protocol, which is sensor measurement values, and falsifying sensor data. Similarly, by falsifying the Modbus function code and data values to disguise the temperature values reflected in the HMI, etc., it may lead to malfunction of valves, etc., resulting in damage to products and manufacturing processes. be.
What are the countermeasures against attacks targeting the core network?
The reason attackers target the core network is that it is an infrastructure that handles information that directly affects the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of the manufacturing process. , the impact of infringement will be large”.
Mr. Ishihara said, ``In this demonstration experiment, it became clear that the core network can be the target system of an attack. mentioned.
For the five attack methods mentioned above, the risk can be reduced by performing encryption and authentication/authorization as follows.
In recent years, "security by design" has been attracting attention as a way of thinking about security measures in systems and products, and this way of thinking is also important in the introduction of local 5G. When implementing PoC, it should be verified including security requirements.
And Mr. Ishihara introduced XDR (cross-layer detection and response), saying that in order to detect anomalies at an early stage, it is necessary to have a mechanism to monitor the whole and detect changes. XDR collects and automatically correlates data across multiple security layers including email, endpoints, servers, cloud workloads and networks. This helps detect threats quickly.
