Performance evaluation of new coronavirus antigen detection reagent
Key points of this research Background Background The importance of accurate, simple, and rapid testing as a measure to prevent infection with the new coronavirus is obvious. Currently, testing using real-time PCR is considered to be the most sensitive and accurate, but the testing method is complicated, costly, and detects even non-infectious virus fragments. . Therefore, Sysmex Corporation has developed the SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test reagent "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent" as a test method used for supplementary diagnosis of novel coronavirus infections. The antigen test using this reagent uses the LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) method, which is a simple and simple nucleic acid detection test for the new coronavirus in nasopharyngeal swabs in a short time by using a fully automatic measurement device. or TMA (Transcription Mediated Amplification) method. This automated antigen detection system uses chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) to specifically detect the proteins of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and can process up to 200 samples per hour. , suitable for large-scale screening tests. In this study, the clinical usefulness of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test reagent "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent", which has the potential to enable rapid and large-scale screening of people infected with the new coronavirus, was investigated. We performed performance evaluations for verification. Details The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) antigen detection reagent "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag reagent" is a nucleocapsid (N) protein (*1) (antigen) possessed by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (Fig. 1, Figure 2) is detected. In this study, we evaluated how accurately this antigen detection reagent could detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in patient nasopharyngeal swabs. First, we confirmed by Western blot analysis (*2) that this reagent accurately detects the N protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Next, we determined the boundary value (cutoff value) (*3) for distinguishing positive from negative when detecting N protein with an automated chemiluminescence detection system using a fully automated immunoassay device.
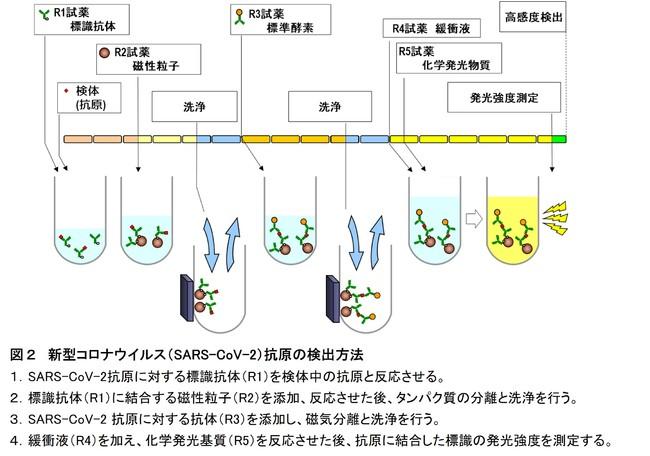
Figure 1 Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) nucleocapsid (N) protein
Figure 2 Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) antigen detection method
A clinical performance study was conducted using 115 nasopharyngeal swabs from 46 patients with a positive COVID-19 PCR test and 69 patients with a negative PCR test. "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent" was found to have high specificity without being positive for other human coronaviruses (*4) that cause common colds and influenza. In addition, all 69 people who were not infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus had negative results. Furthermore, the "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag reagent" was positive in 95.4% of specimens (nasopharyngeal swab) containing 100 or more copies of the RNA gene of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in a PCR test, and the number of copies was 16.6% of the specimens with σ<99 were positive. The cut-off index value (*5) of these positive samples showed a good correlation with the PCR copy number (Fig. 3). Importantly, 81.8% of samples with low viral load (<50 copies) were diagnosed negative. When the viral load is very low, there is almost no infectivity, so this result shows that the "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent" can be usefully used clinically compared to the PCR test.Fig. 3 Correlation between viral protein measurement value by HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag reagent and viral RNA measurement value by RT-PCR method
This research demonstrates that the antigen test using the HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent, which enables rapid measurement of a large number of samples, is suitable for screening tests for infectious new coronaviruses and may be useful for clinical diagnosis. showed gender. Future developments In this study, we demonstrated that an antigen test using a fully automated immunoassay device can rapidly measure a large number of samples with sufficient accuracy, confirming its usefulness as a screening test for clinical diagnosis. "HISCLTM SARS-CoV-2 Ag Reagent" has already been approved for manufacture and sale in Japan as a quantitative reagent, and is being used for screening of the new coronavirus by taking advantage of its characteristics. Since this research was conducted only in Japan, it is hoped that in the future, verification will be carried out in a wider range, such as by conducting verification overseas. In addition, since many mutant strains have appeared in the new coronavirus, it is necessary to verify that accurate measurement can be performed even with various mutant strains. In addition, in any test, cases with a low viral load will be below the detection limit (negative), and the amount of viral shedding changes over time even in the same subject, so it is necessary to collect samples at appropriate times. there is. It is necessary to understand the characteristics (sensitivity, specificity, rapidity, etc.) of each testing method, and to operate appropriately to improve the efficiency and accuracy of testing. Glossary *1 Nucleocapsid protein: One of the proteins that make up coronavirus. Structural proteins of the new coronavirus include spike protein, envelope protein, membrane protein, and nucleocapsid protein. *2 Western blot analysis: A method of detecting specific proteins using antigen-antibody reactions. *3 Cut-off value: A numerical value that distinguishes between positive and negative test results. *4 Human coronavirus: Other than the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), there are four types of coronaviruses that infect humans that cause colds (HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV -HKU1) and two severe pneumonia viruses (SARS-CoV, MARS-CoV) transmitted from animals are known. *5 Cut-off index (COI): The luminescence intensity of a sample when the luminescence intensity of the cut-off value is 1.0, and indicates the amount of antigen detected. * HISCL is a registered trademark of Sysmex Corporation. Original article The results of this research were published in the online version of the British scientific journal Scientific Reports (December 1, 2021). Paper title: Performance and usefulness of a novel automated immunoassay HISCL SARS-CoV-2 Antigen assay kit for the diagnosis of COVID-19 Author: Kaori Saito, Tomohiko Ai, Akinori Kawai, Jun Matsui, Yoshiyuki Fukushima, Norihiro Kikukawa, Takuya Kyoutou, Masayoshi Chonan, Takeaki Kawakami, Yoshie Hosaka, Shigeki Misawa, Haruhi Takagi, Yasushi Matsushita, Makoto Hiki, Atsushi Okuzawa, Satoshi Hori , Toshio Naito, Takashi Miida, Kazuhisa Takahashi, Yoko Tabe Masayoshi 3, Takeaki Kawakami 3, Yoshie Hosaka 3, Shigeki Misawa 3, Yo Takagi 4, Yasushi Matsushita 5, Makoto Hiki 6, Junji Okuzawa 7, 8, Ken Hori 9, Toshio Naito 8, 10, Takashi Miida 1, Kazuhisa Takahashi4,8, Yoko Tabe1,8, Affiliation: 1) Department of Clinical Laboratory Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Juntendo University, 2) Sysmex Corporation, 3) Department of Clinical Laboratory, Juntendo University Hospital, 4) Graduate School of Medicine, Juntendo University Department of Respiratory Medicine, 5) Department of Collagen Medicine, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, 6) Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, 7) Center for Innovative Medical Technology Development, Juntendo University, 8) Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine 9) Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Department of Infection Control Science, 10) Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Department of General Medicine DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-02636-x