Ability of antivirus and firewall / IPS
Now that you have successfully prepared the SEPM and deployed the SEP client, let's take a look at the settings of each function and the design of the policy.
Virus / spyware protection that reliably blocks malicious programs
Anti-virus and anti-spyware are the basic security functions. As you know, Symantec's antivirus technology has been installed in personal products for a long time, and boasts a high detection rate due to the automatic update of the definition file of "LiveUpdate".
As a policy of such anti-virus / spyware function, scheduling by scheduled scan, on / off of Auto-Protect which is real-time scan for file system and e-mail, action when malware etc. are detected can be set. As expected, it has a long history, and you can make detailed settings such as whether to scan compressed files and the CPU usage rate. Since it is difficult for the end user to change these settings, it is possible to lock them so that they cannot be changed by the SEP user. Conversely, you can set a policy that allows users to arbitrarily postpone scanning when they are away from home.
Click "Policy"-"View Policy"-"Antivirus and Antispyware" for settings.
In addition to such definition file-based detection and removal, SEP has a "proactive threat prevention" function that prevents malicious programs and attacks that are not registered in the database. Proactive means "preventive" and refers to the ability to detect viruses and spyware without using a definition file. These technologies have received a great deal of attention due to the large number of viruses and spyware that can be bypassed by definition files.
Specifically, it monitors the behavior of more than 120 types of processes, scores both good and evil behavior, and finds malicious programs. It is possible to detect malicious programs such as Trojan horses, worms, keyloggers, and spyware without relying on definition files. It also checks the Windows API, such as accessing files and registries and loading DLLs, to see if there are any programs that behave suspiciously.
Screen 2 You can edit each policy from the menu displayed on the left.
Suspicious files detected as viruses or spyware can, of course, be cleaned (repaired), but you can also select "quarantine". In other words, once you quarantine the suspicious file, check it, and then take appropriate action.
There are two methods of quarantine: local quarantine, which is saved as an infeasible format on the local hard disk, and transmission to a separately constructed "central quarantine server". When sent to the central quarantine server, it sends the infected file to the Security Response Center, a Symantec lab. The Response Center will check the file and return a new definition file that reflects this.

Network threat prevention that combines firewall and IPS
Network threat prevention prevents network attacks called cracking and unauthorized access. There are two types of firewalls: a firewall that blocks unauthorized packets based on IP addresses and ports, and an intrusion prevention system (IPS) that exposes attacks from traffic based on signatures that create a database of attack methods, similar to antivirus measures. Use technology. Simple port-based firewalls are also installed in Windows and other devices, but SEP offers a higher degree of protection.
First, for the firewall, select "Policy"-"View Policy"-"Firewall", and edit the existing policy or add a new policy from "Tasks". Firewall policies include "rules" that condition and allow traffic to and from, "smart track filters" that allow applications such as DHCP, DNS, and WINS commonly used in IP networks, and special traffic. "Traffic and stealth settings" that control the network and hide the information written in the HTTP header are provided.
In the firewall rules, by combining four "triggers", "application", "host (destination / source IP address)", "network service (destination / source port)", and "blank (no setting)", Detailed traffic management can be performed. Of these, the "application" trigger, which is not installed in packet filtering-based firewalls, is quite unique. By using this, even with HTTP communication using the same port 80, it is possible to control Internet Explorer to allow and Firefox to prohibit.
These rules can be changed not only on the server side but also on the client side so that the rules can be changed.
Easy-to-understand firewall policy settings with heavy use of screen 3 icons
These policies vary by organization, department, and where they apply. For example, you may want to change the firewall rules for internal clients under the firewall and for clients on the go. In response to these needs, SEP has an "autolocation switching" function that automatically identifies the location from the network state and changes the policy to be applied. To take advantage of this feature, you should set multiple policies for internal and on-the-go. In addition, when operating NAC (Network Access Control), which will be described later, it is better to create an isolation policy for PCs that do not meet the security policy.
Similarly, intrusion prevention can be added or edited from the "Intrusion Prevention" menu. In addition to so-called signature-based intrusion prevention, you can set whether to detect DDoS attacks and port scans. You can also create custom signatures for application-specific attacks.
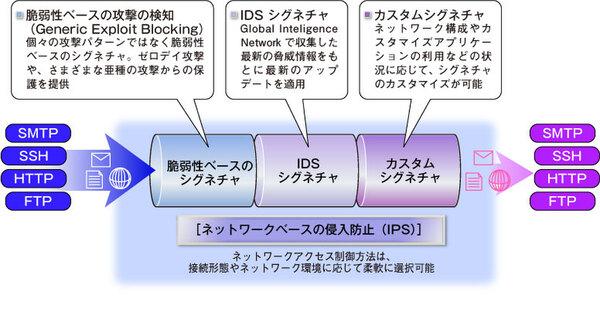
Figure 2 Unauthorized access protection with IPS introduced in SEP
Screen 4 Generated 4 policies with different strengths according to the application
For IPS signatures, you can also create your own custom signatures. In the demo, in the example of "blocking communication to 2channel", we asked them to create a signature that prohibits communication when there is a character string of 2ch.net when sending via HTTP.
Screen 5 You can easily create a signature that prohibits the connection of 2ch.net.
■ Related sites
